AMOLED vs OLED – An Overview of Different Types of Display Technologies

The role of display in our lives is very important. Display means a well-organized representation of data that is available in the form of text, images, and graphics. Different devices are available that can present the information to the users that can be visualized by human eyes.
The display devices that require electric signals as input to provide information to the users are called electronic display devices.
Technology is revolutionizing in every field of life. The invention of display technology also affects display devices. The manufacturers then focus on the development of new display devices that are compatible with the latest display technologies, to follow the trend.
Every technology has many features in terms of its time. In this topic, we will discuss different types of display technologies, their features, a comparison between them, and their use in different electronic visual display devices.
Different types of display technologies
Two different display technologies are available nowadays and are being used in electronic visual displays:
- Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
- Light Emitting Diode (LED) Display
1. Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
It is an electronic visual display that enables users to view text, images, videos, or any other visual objects by changing the frequency, intensity, phase, and amplitude of light along with changing the polarization of radiated oscillations.
We can also say that it works with polarizers by using light modulating properties. LCD is flat and lighter than previously used Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) in televisions for display. It produces colorful images by using a backlight or reflector without emitting light.
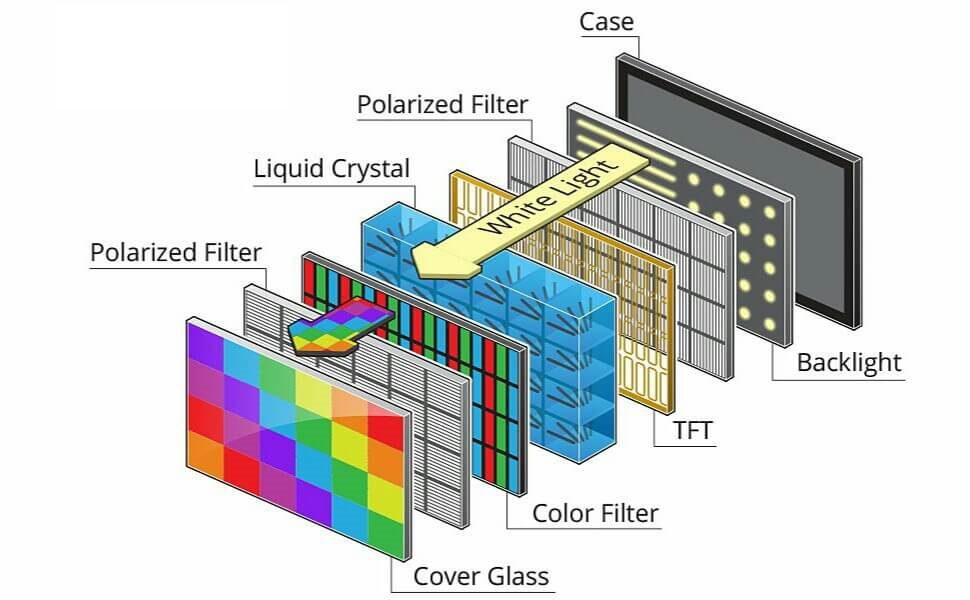

The LCD screen is used in various electronic display devices such as calculators, mobiles, laptops, digital cameras, digital watches, and so on. This display technology is classified into further categories which are listed below:
a). Light Emitting Diode (LED) Backlit LCD
A type of LCD technology in which LEDs are used in backlighting instead of CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent). This technology is slim, lighter, consumes less power, and has a great contrast ratio as compared to common LCD.
b). Thin Film Transistor (TFT) LCD
In this category, image quality is improved by using thin-film transistor technology. Transistors are used to control every pixel in the display screen, resultantly, response time increases. Twisted nematic, In-Plane Switching (IPS), and Plane Line Switching (PLS) are the most known types of TFT LCD.
c). Quantum dot (QLED) Display
The combination of the properties of light and electricity are used in this display that makes use of semiconductors particles which are very small (nanometers) in size, to react. Each pixel on the display emits red, green, or blue light or a combination of these colors.
The consistency of the color of every pixel is determined by Wavelengths. Semiconductor particles can be easily adjusted to their desired size to release different wavelengths for optimal color creation.
Keeping in view the many types of display technologies, it becomes very difficult to select the best one. The display screen which has the most features in terms of power, refresh rate and provides the best result to our eyes will be considered the best one (by ignoring the price factor).
2. Light Emitting Diode (LED) Display
This technology displays visual objects by using lights as an emitting source when an electric current is supplied. The Light-emitting diodes allow passing the current in a forwarding direction only. Therefore we can say that the characteristics of LED are very similar to PN Junction that blocks the current when it flows in the reverse direction.
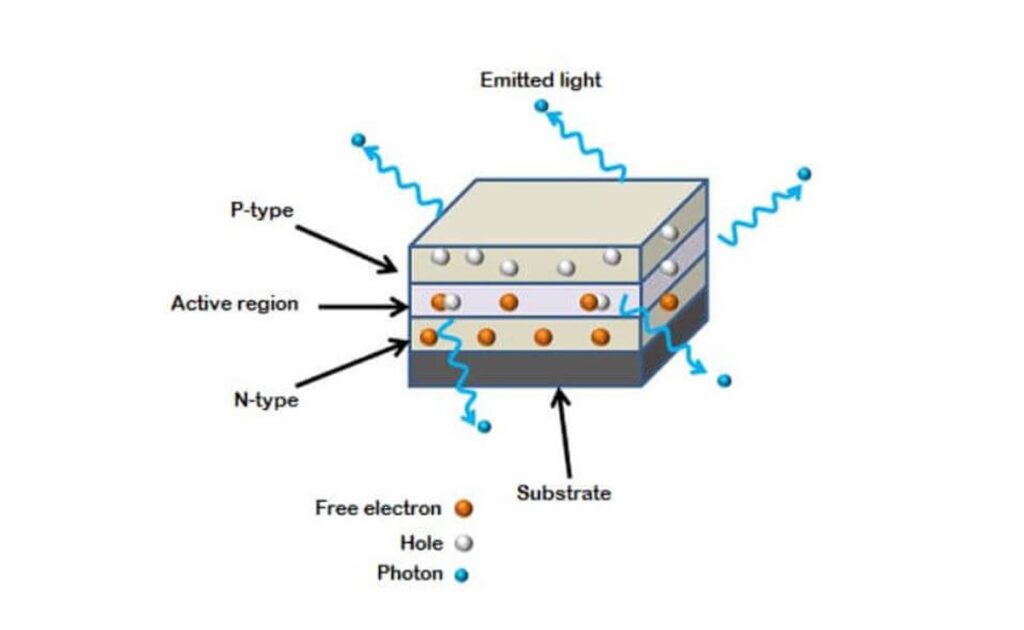

Light-emitting diodes combine the P-type semiconductors (holes) with N-type semiconductors (electrons) and make a PN Junction when a sufficient voltage is applied.
The applications of LEDs are the same as LCDs and are commonly used in TVs and color displays.

LED Display is further subdivided into three categories due to its various extended versions of display technologies:
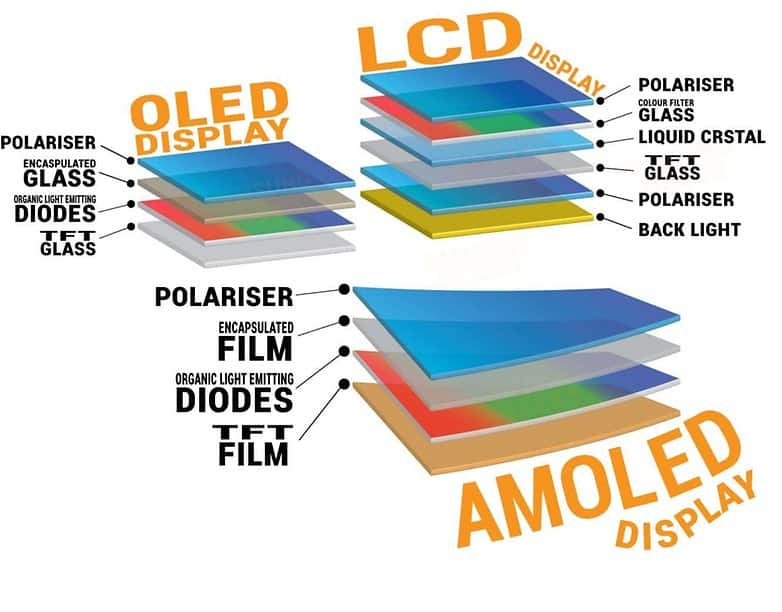
a). Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) Display
It is also known as an organic electroluminescent diode. In this display, a film of organic compounds is used to emit light.
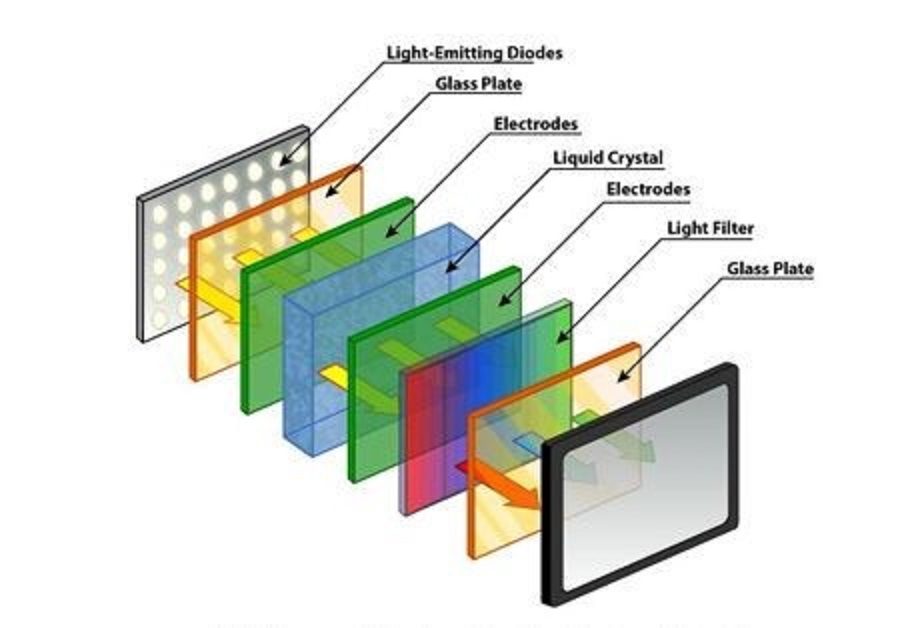
OLED display does not use backlight however it uses visible light. In this display, every pixel comprises a color filter, a liquid crystal, and a tiny light.
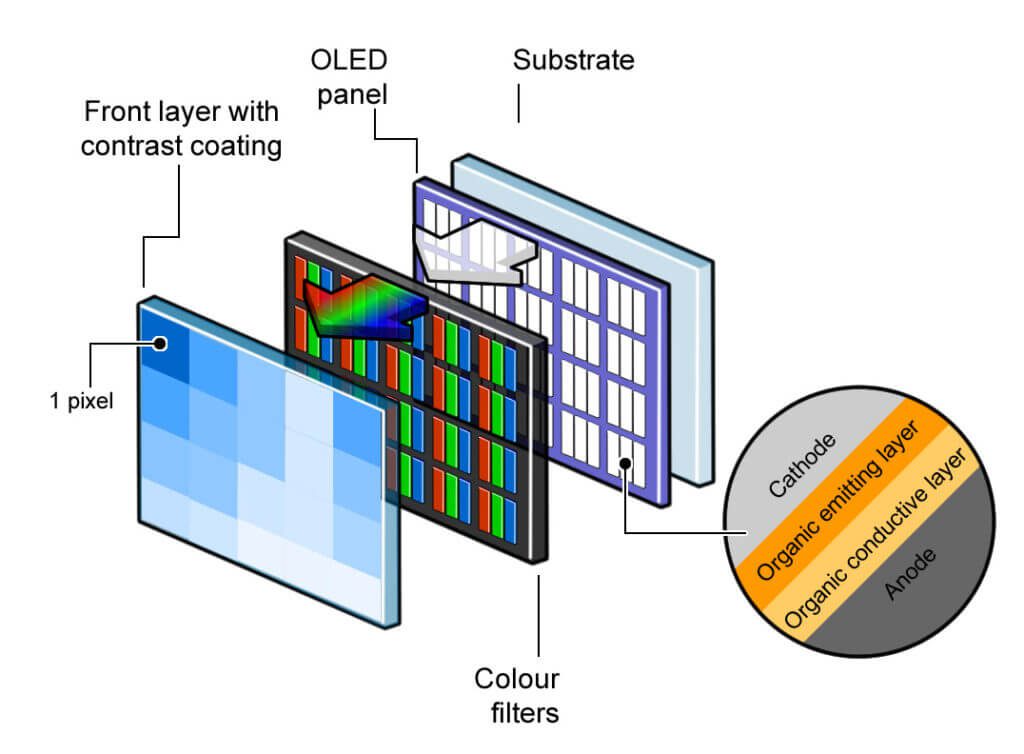

Liquid crystal comprises the specifications of solid and liquid. It does not allow to pass light when it is in liquid form and blocks when it is in the solid-state.
The working of the liquid pixel is like an aperture. The liquid crystal changes its state from liquid to solid by applying electric current when pixels have to display color on the screen.
Then the light enters through the liquid crystal and the color filter makes it colored that becomes visible.
b). Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode (AMOLED) Display
AMOLED display comprises the features of OLED display technology in addition to the thin-film transistors (TFT) layer behind each pixel.
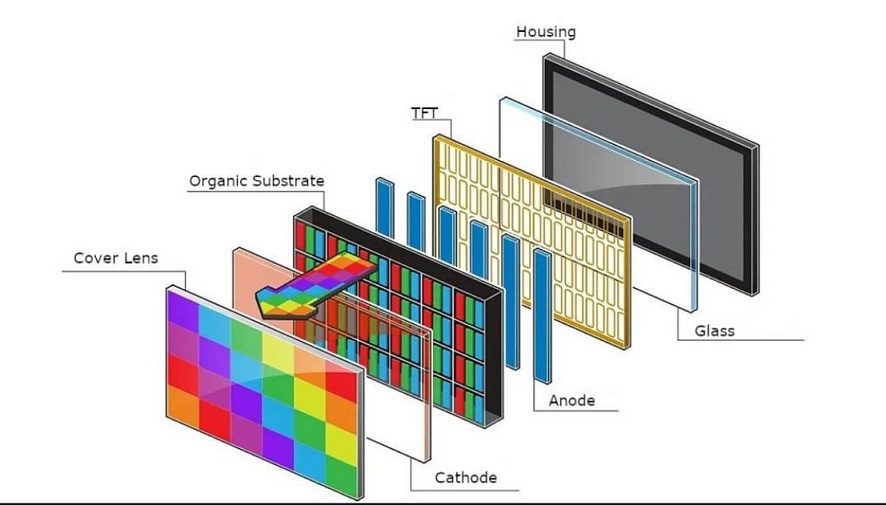

Transistors are very helpful in quickly moving the electric current across the entire display. It is most commonly used for large displays where it can transfer the current rapidly to the entire screen and an enhanced refresh rate can be maintained.
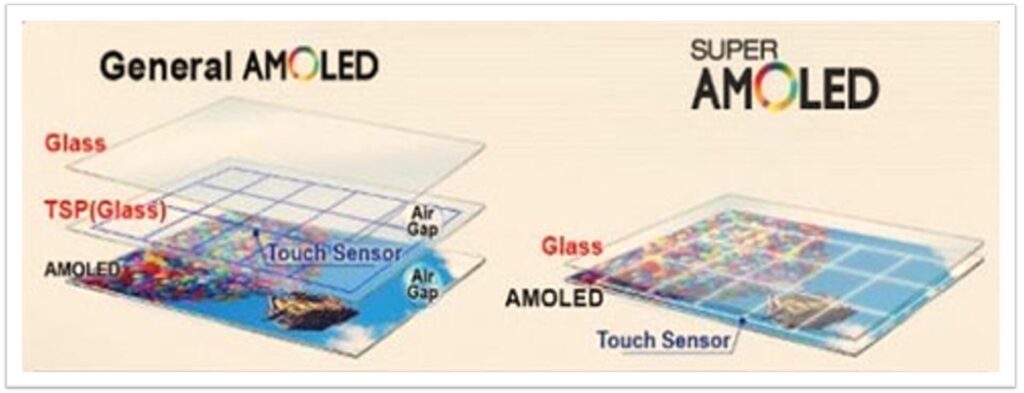
c). Supper AMOLED Display
It is an advanced version of AMOLED display that is being used in popular smartphones. This is an AMOLED display with an integrated touch screen function.
The touch screen functionality is also available in the AMOLED technology, however, its touch-sensitive layer is located specifically on top of the screen whereas, in Super AMOLED displays, the layer is built into the screen.
The Super AMOLED displays become easier to view in direct sunlight if the extra layer is removed. This is the more desirable feature in today’s mobile phones.
Comparison – AMOLED vs OLED
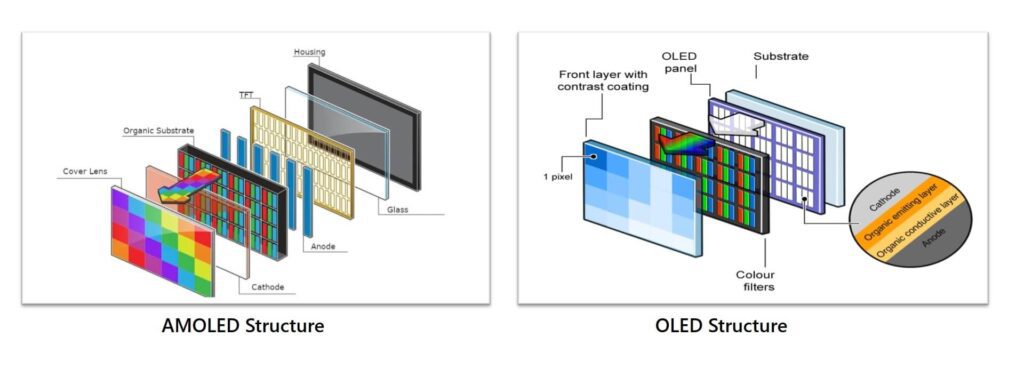

AMOLED displays are one step higher than OLED display technology. The key differences between them are categorized as under:
| Parameters | AMOLED | OLED |
| Display technology | OLED features in addition to Thin Film Transistors (TFTs) | A thin layer of organic compound |
| Material | Active Matrix System | The organic material to emit the light |
| Battery usage | Low | High |
| Refresh Rate | High refresh rate (which provides smooth graphics in gaming and videos) | Less refresh rate as compared to AMOLED display |
| Display angles | Provides multiple display angles to view the screen. | Limited viewing angles than AMOLED display |
| Energy efficiency | Less energy efficient | High energy efficient as compared to AMOLED |
| Cost | High | Economical than AMOLED |
| Quality | Sharp and better picture quality | Moderate picture quality |
| Display size | Supports high resolution and large displays as compared to OLED | Provides large, thinner, and efficient displays as compared to LCDs, but not suitable for a wide range of displays |
| Flexibility | More flexible than OLED | Less Flexible than AMOLED |
AMOLED vs Super AMOLED

| Parameters | AMOLED | Super AMOLED |
| Display technology | Thin Film Transistors Layer | Integrated touch screen digitizer |
| Accessibility | Moderate visibility in direct sunlight | Easier to display in direct sunlight |
| Competitor | Best competitor of OLED | Best competitor of AMOLED |
| Power consumption | Require more power to display | Require less power to display |
| Touch Functionality | Hard touch | Smooth touch functionality |
| Cost | Economical than super AMOLED | Expensive |
| Picture Quality | Good | Excellent |
The AMOLED and Super AMOLED display technologies are used in very large displays, laptops, mobile phones, tablets, TVs, digital cameras, calculators, industrial digital machines, etc.




